Investor Due Diligence Checklist: Your Essential Guide
Last Revised: May 6, 2025Unlocking Smart Investments: Your Due Diligence Guide
In the world of finance, due diligence is essential for making sound investment decisions. It’s the foundation upon which informed choices are built, protecting investors from unforeseen risks. From examining balance sheets to assessing ethical implications, due diligence has evolved into a multifaceted process. Today, it’s more critical than ever for strategically allocating capital and maximizing returns.
Effective due diligence requires a comprehensive approach that adapts to the evolving investment landscape. It’s no longer sufficient to simply review financial statements. A thorough strategy considers various factors, including the management team’s expertise, the business model’s robustness, current market trends, and the increasing focus on sustainability.
This guide presents a comprehensive investor due diligence checklist, covering eight crucial areas of investigation. Whether you’re a seasoned CFO, Head of Compliance, or Investor Relations Manager, understanding these key areas will empower you to make smart investments.
Eight Essential Areas of Due Diligence
- Financial Analysis: A deep dive into financial statements (income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement) to assess the company’s financial health and performance.
- Market Research: Understanding the target market, competitive landscape, and industry dynamics to evaluate the investment’s potential for growth and profitability.
- Legal Review: Examining legal documents, contracts, and regulatory compliance to identify potential legal risks and liabilities.
- Management Evaluation: Assessing the experience, track record, and integrity of the management team to gauge their ability to execute the business plan.
- Business Model Analysis: Evaluating the company’s business model, revenue streams, and competitive advantages to determine its long-term viability.
- Operational Due Diligence: Reviewing the company’s operations, processes, and infrastructure to identify potential operational risks and inefficiencies.
- Technology Assessment: Evaluating the company’s technology, intellectual property, and innovation capabilities to assess its competitive edge.
- Ethical Considerations: Examining the company’s ethical practices, social responsibility, and environmental impact to ensure alignment with investor values.
By mastering these eight areas, you can confidently navigate the complexities of today’s dynamic market and make informed investment decisions with greater foresight. This comprehensive approach will help you unlock smart investments and achieve your financial goals.
1. Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis is essential for any serious investor conducting due diligence. It involves a deep dive into a company’s financial reports—balance sheets, income statements, cash flow statements, and projections—to evaluate its financial health, potential for growth, and any associated risks. This crucial step empowers investors to make well-informed decisions based on concrete data, not just speculation, securing its place at the top of every due diligence checklist.
Key Components of a Thorough Analysis
A truly comprehensive financial statement analysis covers several key areas:
- Historical Review (3-5 Years): Analyzing trends in key metrics over several years can reveal patterns and potential weaknesses.
- Cash Flow: Understanding a company’s cash generation and usage is vital for assessing its liquidity and long-term viability.
- Debt: Evaluating a company’s debt levels and repayment terms helps determine its financial leverage and risk.
- Revenue Streams: Identifying revenue sources and their stability offers valuable insights into the business model and its future.
- Profit Margins: Analyzing profit margins helps assess a company’s efficiency and pricing strategies.
- Capital Expenditures: Understanding investment in fixed assets reveals a company’s growth strategy and future plans.
Advantages of Financial Statement Analysis
Conducting a thorough analysis offers a number of benefits:
- Data-Driven Decisions: It provides quantifiable data, reducing emotional or biased investment decisions.
- Historical Insights: It reveals trends in revenue, profitability, and cash flow, allowing for more informed predictions.
- Risk Identification: It can uncover warning signs like questionable accounting, high debt, or declining profits.
- Accurate Valuation: It forms the basis for determining a company’s true worth and pinpointing investment prospects.
Limitations of Financial Statement Analysis
While valuable, this approach has limitations:
- Past Performance: Strong historical performance doesn’t guarantee future success.
- Accounting Methods: Variations in accounting practices can make comparing different companies difficult.
- Specialized Knowledge: Understanding complex statements may require the expertise of a financial analyst.
- Private Company Data: Obtaining detailed financial data for private companies can be challenging.
Real-World Applications
Financial statement analysis has played a key role in many high-profile investment decisions:
- Warren Buffett and Coca-Cola: Buffett’s careful study of Coca-Cola’s financials, especially its consistent cash flow, underpinned Berkshire Hathaway’s significant investment.
- SoftBank and WeWork: SoftBank’s due diligence on WeWork uncovered significant financial inconsistencies and unsustainable practices, leading to the withdrawal of its IPO.
- Private Equity Firms: Firms like KKR use standardized financial analysis frameworks for rigorous and objective evaluation of potential investments.
Practical Tips for Conducting Analysis
Here are some practical tips to improve your analysis:
- Benchmarking: Compare the company’s performance to industry averages.
- Verification: Cross-check reported numbers with external sources like industry reports or SEC filings.
- Cash Flow Focus: Prioritize cash flow over just revenue or profit.
- Earnings Quality: Scrutinize earnings consistency to detect any potential manipulation.
- Expert Advice: Consult a forensic accountant for complex investments.
Historical Context and Modern Usage
Benjamin Graham’s value investing philosophy, which emphasized intrinsic value, greatly popularized financial statement analysis. Warren Buffett, following Graham’s principles, refined this approach, showcasing its efficacy. Consulting giants like McKinsey & Company have also furthered the adoption of robust frameworks in corporate valuation.
For financial professionals like Chief Compliance Officers, Heads of Compliance, Compliance Directors, CFOs, and Investor Relations Managers, a deep understanding of financial statement analysis is critical. It facilitates sound decision-making, mitigates risk, and helps identify worthwhile investment opportunities. By diligently applying these principles, investors can navigate the financial world and enhance their chances of success.
2. Management Team Assessment
A solid investor due diligence checklist needs a thorough Management Team Assessment. This critical step involves more than just glancing at resumes. It’s a deep dive into the leadership team’s experience, their track record, their integrity, and, perhaps most importantly, their ability to execute the business plan.
For key stakeholders like CFOs, Compliance Officers, and Investor Relations managers, understanding the management team is paramount. This assessment scrutinizes executives’ qualifications, analyzes past performance, and evaluates their vision for the future.
Key Features of a Management Team Assessment
- Background Checks on Key Executives: This helps identify any potential legal or ethical risks.
- Leadership Team’s Industry Experience: Relevant experience and industry knowledge are vital for success.
- Track Record of Previous Ventures: Past performance offers insight into the team’s abilities. Were prior ventures successful? If not, what were the contributing factors?
- Compensation Structure Alignment With Company Goals: Tying compensation to performance incentivizes the team.
- Management Retention and Turnover Patterns: High turnover might signal internal problems.
- Succession Planning: A clear plan shows foresight and mitigates risk.
Pros of Conducting a Management Team Assessment
- Strong Management Often Correlates With Company Success: Skilled leadership can drive business growth.
- Reveals Potential Character or Competence Issues: Due diligence can uncover red flags.
- Helps Assess Leadership’s Ability to Navigate Challenges: Past performance reveals problem-solving skills.
- Provides Insight Into Company Culture: Management sets the tone for the organization.
Cons of Relying Solely on Management Team Assessment
- Subjective Assessment Factors: Evaluating leadership can be subjective and prone to bias.
- Past Success Doesn’t Guarantee Future Performance: Market conditions and other factors can impact outcomes.
- Difficult to Evaluate Team Dynamics From the Outside: Internal relationships are hard to assess externally.
- May Overweight Charismatic Leaders Versus Operational Excellence: Charisma isn’t a substitute for execution.
Real-World Examples
- Sequoia Capital‘s in-depth vetting of Airbnb’s founders exemplifies thorough due diligence.
- Andreessen Horowitz‘s founder-focused approach underscores the importance of strong teams.
- Blackstone‘s assessment of Hilton Hotels before acquisition demonstrates the value of leadership evaluation.
Practical Tips for Implementing a Management Team Assessment
- Interview Former Colleagues, Employees, and Business Partners: Diverse perspectives provide a holistic view.
- Research Leaders’ Previous Ventures and Exits: Contextualizing past performance is critical.
- Assess How the Team Handles Tough Questions: Transparency and problem-solving abilities are revealed under pressure.
- Evaluate Alignment Between Executives’ Incentives and Investor Interests: Shared goals are crucial.
- Look for Complementary Skills Across the Leadership Team: Diverse skill sets contribute to overall success.
Influential Figures and Frameworks
Authors like Jim Collins, who wrote “Good to Great”, highlight the importance of Level 5 leadership. Peter Thiel, co-founder of PayPal, emphasizes team assessment. John Doerr’s focus on management evaluation at Kleiner Perkins further solidified this practice.
In conclusion, a thorough Management Team Assessment is an essential part of any investor’s due diligence process. By carefully evaluating the leadership team, investors can significantly mitigate risk and enhance the probability of positive outcomes.
3. Market Analysis and Competitive Landscape
A thorough market analysis and competitive landscape assessment are essential for sound investment decisions. This process goes beyond simply understanding the product or service; it digs deep into market dynamics. This provides crucial context for a company’s potential growth and profitability. For key stakeholders like compliance officers, CFOs, and investor relations managers, this step is vital for managing risk and aligning with investment goals. It ensures investors can gauge the true potential of an opportunity within the broader market.
This analysis involves researching the company’s target market size, its potential for growth, its competitive position, and the overall industry trends. It specifically looks at market trends, competitor strengths and weaknesses, and the company’s unique value proposition.
Key Features of Market Analysis
- Total Addressable Market (TAM) Calculation: This determines the total revenue opportunity within the market.
- Market Growth Rate Analysis: This evaluates the market’s historical and projected growth.
- Competitive Positioning Assessment: This clarifies the company’s standing compared to its competitors.
- Barriers to Entry Evaluation: This identifies obstacles preventing new competitors from entering the market.
- Industry Disruption Potential: This assesses the likelihood of disruptive innovations impacting the market.
- Regulatory Environment Impact: This analyzes how current and future regulations could influence the market.
Pros of Market Analysis
- Contextualizes Company Growth Potential: Provides a realistic view of achievable growth.
- Identifies Market Saturation Risks: Highlights potential growth limitations due to market maturity.
- Reveals Competitive Advantages and Vulnerabilities: Pinpoints strengths and weaknesses compared to competitors.
- Helps Assess Business Model Scalability: Determines if the business model can expand to capture more market share.
Cons of Market Analysis
- Market Size Estimates Can Vary: Different sources and methods can create discrepancies in market sizing.
- Fast-Changing Markets Can Invalidate Analysis: Rapid industry evolution can quickly make initial assessments outdated.
- Predicting Disruptive New Entrants Is Difficult: Unforeseen innovations can significantly change the competitive landscape.
- International Markets Require Specialized Knowledge: Analyzing foreign markets presents unique challenges, requiring cultural and economic understanding.
Real-World Examples
- Silver Lake Partners and Alibaba: Silver Lake Partner’s investment in Alibaba demonstrates the importance of thorough market analysis. Their research into the growing Chinese e-commerce market was a critical factor in their investment success.
- Benchmark Capital and Uber: Benchmark Capital’s investment in Uber highlighted the value of understanding the competitive landscape. By mapping the taxi and transportation industry, they recognized Uber’s disruptive potential.
- Tiger Global’s Tech Investments: Tiger Global’s use of systematic market sizing, including TAM calculations and growth projections, has been key to their successful technology investments.
Tips for Implementing Market Analysis
- Use Multiple Sources: Cross-referencing data from various research firms, industry reports, and competitor analyses helps ensure accuracy.
- Conduct Interviews: Gaining insights from industry experts and customers provides valuable perspectives on market trends and customer needs.
- Analyze Competitor Performance: Benchmarking the company’s growth and profitability against its rivals helps identify areas for improvement and potential competitive advantages.
- Consider Future Changes: Anticipating technological or regulatory changes is crucial for long-term success.
- Identify Sustainable Competitive Advantages: Understanding what differentiates the company and protects it from competition is essential.
Influential Frameworks and Methodologies
Influential figures and frameworks like Michael Porter’s Five Forces, Clayton Christensen’s disruption theory, and Marc Andreessen’s market analysis methodology provide structured approaches to understanding market dynamics. By incorporating these frameworks and applying the tips above, investors can gain deeper insights and make more informed decisions.
4. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Legal and regulatory compliance due diligence is essential to any investment decision. It’s a thorough investigation of a company’s legal standing, including regulatory adherence, pending litigation, intellectual property (IP) rights, and contractual obligations. This process confirms the company operates legally, identifies potential legal risks, and protects the investor from unexpected liabilities. Overlooking this crucial step can lead to expensive legal battles, regulatory penalties, or even a complete loss of investment.
Why is this so important for your due diligence checklist? Unforeseen legal problems can derail even the most promising investments. A seemingly small issue can escalate into costly litigation, fines, or reputational damage, severely impacting returns. Legal due diligence mitigates this risk by proactively identifying potential issues.
Key Features of Legal and Regulatory Due Diligence
- Litigation History and Pending Lawsuits: Examining past and current legal disputes helps assess the company’s litigation risk and potential financial impact.
- Intellectual Property Portfolio and Protection: Verifying ownership and validity of patents, trademarks, and copyrights secures the company’s competitive edge and protects its core assets.
- Corporate Governance Structure: Analyzing the company’s board structure, bylaws, and decision-making processes uncovers potential conflicts of interest or weaknesses in corporate oversight.
- Regulatory Approvals and Compliance: Confirming adherence to industry-specific regulations and licensing is critical, particularly in heavily regulated sectors like finance and healthcare.
- Material Contracts Review: Scrutinizing key customer, vendor, and employment contracts reveals potential liabilities or restrictions from change-of-control provisions or other clauses.
- Employment Practices Compliance: Reviewing adherence to labor laws, including wage and hour regulations, discrimination policies, and workplace safety is key to avoiding future legal problems.
Pros of Legal Due Diligence
- Identifies Potentially Costly Legal Issues: Proactive identification allows for negotiating safeguards or even deal termination before substantial investment.
- Ensures Intellectual Property Protection: Validating IP ownership protects the investor’s stake in the company’s core innovations.
- Prevents Regulatory Surprises: Thorough compliance review minimizes the risk of unexpected fines, penalties, or operational disruptions.
- Validates the Company’s Right to Operate: Ensures the company has the necessary licenses and permits, protecting business continuity.
Cons of Legal Due Diligence
- Cost and Time: Legal reviews can be expensive and time-consuming due to their complexity.
- International Operations: Navigating different legal systems and regulations for international operations adds complexity and cost.
- Evolving Regulations: Keeping up with changes in legal and regulatory landscapes can be challenging.
- Quantifying Risk: Assessing the potential financial impact of some legal issues can be subjective and uncertain.
Real-World Examples
- Google and Motorola Mobility: Before acquiring Motorola Mobility, Google conducted extensive due diligence on its patent portfolio to understand its value and potential legal risks.
- Microsoft and LinkedIn: Microsoft meticulously reviewed LinkedIn’s data privacy practices and regulatory compliance before the acquisition.
- Thoma Bravo and Software Companies: Thoma Bravo, a private equity firm, developed a robust legal due diligence framework for the software industry.
Practical Tips for Implementation
- Specialized Legal Counsel: Engage legal counsel with expertise in the relevant industry.
- Warranty Coverage: Request warranty coverage for undisclosed legal issues from the target company.
- IP Verification: Thoroughly review all IP documentation to confirm ownership and validity.
- Regulatory Compliance Assessment: Ensure compliance with all applicable laws and regulations in every operational region.
- Contract Review: Review key customer and vendor contracts for change-of-control provisions.
Influential Frameworks and Guidelines
While no single website serves as a central repository, leading law firms shape the field. Firms like Wilson Sonsini Goodrich & Rosati, known for its tech industry work, Wachtell, Lipton, Rosen & Katz, renowned for its M&A expertise, and the American Bar Association, which publishes various guidelines, influence best practices. Their established precedents have formalized the role of legal and regulatory compliance in investment due diligence.
5. Business Model Validation
Business Model Validation is a critical component of any robust investor due diligence checklist. It dives into the core of a company’s operations, examining how it creates, delivers, and captures value. This goes beyond simply understanding the product or service; it requires a thorough analysis of the mechanics driving revenue, managing costs, and generating profit. For key players like the Chief Compliance Officer, Head of Compliance, Compliance Director, CFO, or Investor Relations Manager, understanding the robustness and sustainability of a business model is paramount to informed decision-making and risk mitigation.
This validation process scrutinizes several key areas:
- Revenue Model Analysis: Understanding the various revenue streams, their individual contributions, and their long-term potential. This includes recurring revenue models like subscriptions, transactional revenue, and advertising revenue.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) Evaluation: Determining the cost of acquiring a new customer is crucial for assessing marketing and sales efficiency. A high CAC can be a warning sign, indicating potential scalability challenges.
- Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) Calculation: Estimating the total revenue generated by a customer throughout their relationship with the company. A healthy LTV:CAC ratio (typically 3:1 or higher) is essential for sustainable growth.
- Unit Economics Breakdown: Analyzing the profitability of individual business units (e.g., per customer, per product). This detailed view helps identify cost drivers and potential areas for optimization.
- Pricing Strategy Assessment: Evaluating the effectiveness and sustainability of the company’s pricing model. This includes analyzing price elasticity, competitor pricing, and the potential impact of price changes on demand.
- Scalability Factors: Identifying factors that could limit or facilitate the company’s ability to grow its operations and revenue. This involves analyzing resources, processes, and infrastructure.
Why Is This Crucial for Due Diligence?
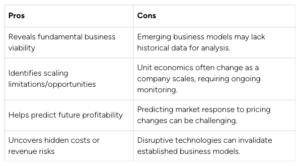
Business Model Validation reveals the fundamental viability of a company. It allows investors to identify potential scaling limitations or opportunities, predict future profitability, and uncover hidden costs or revenue risks. By understanding these core elements, investors can make more informed decisions and mitigate potential losses.
Pros and Cons of Business Model Validation
Here’s a quick look at the advantages and disadvantages:
Real-World Examples
- Andreessen Horowitz‘s deep dive into Airbnb‘s marketplace economics played a crucial role in their investment decisions, demonstrating the power of understanding the platform’s network effects and scalability.
- Amazon‘s meticulous validation of Whole Foods‘ business model before acquisition underscores the importance of scrutinizing even established businesses for potential synergies and growth opportunities.
- Insight Partners’ SaaS business model evaluation framework provides a structured approach to assessing key metrics like churn, LTV, and CAC, enabling them to make data-driven investment decisions.
Tips for Implementation
- Test assumptions with sensitivity analysis: Understand how changes in key variables (e.g., CAC, churn rate) impact overall profitability.
- Compare unit economics to industry benchmarks: Assess the company’s performance relative to its competitors.
- Validate CAC and LTV ratios through multiple methods: Ensure accuracy and avoid relying on single-point estimates.
- Understand revenue recognition policies: Ensure compliance and transparency in financial reporting.
- Analyze potential network effects or economies of scale: Identify potential competitive advantages and growth drivers.
Evolution and Popularization
The concept of Business Model Validation gained significant traction with the popularization of tools like Alex Osterwalder’s Business Model Canvas, which provides a visual framework for mapping key business components. Bill Gurley’s emphasis on unit economics and David Skok’s SaaS metrics analysis further refined the approach, providing practical frameworks for evaluating the financial viability of different business models.
By incorporating Business Model Validation into your due diligence process, you can significantly reduce risk and improve the likelihood of successful investments. This step is not just about understanding what a company does, but also how it does it, and crucially, whether that model can deliver sustainable, long-term value.
6. Technology and Operational Assessment
A robust technology and operational assessment is crucial for informed investment decisions. This due diligence step digs into the core of a company’s technical infrastructure, product development methodology, operational processes, and scalability potential. It aims to understand not just what a company claims to do, but how it achieves those claims, and if its technology can support its growth ambitions. For compliance professionals, CFOs, and investor relations managers, understanding this assessment is vital for accurately representing a company’s capabilities and mitigating potential risks.
Key Features of the Assessment
This assessment examines several key areas:
- Technology Architecture Review: Evaluating the underlying technology stack, its design, and how well it fits the company’s business model.
- Product Development Methodology: Assessing the company’s approach to building and improving products, including Agile, Waterfall, or other methodologies.
- IT Security and Data Protection Practices: Examining the company’s cybersecurity posture, data privacy measures, and compliance with relevant regulations.
- Operational Efficiency Metrics: Analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) related to production, delivery, customer service, and other core operational functions.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Evaluating the strength and flexibility of the company’s supply chain, considering potential disruptions and dependencies.
- Technical Debt Assessment: Identifying and quantifying the impact of accumulated technical compromises made for short-term gains, which can affect future development speed and cost.
Why This Matters in Due Diligence
This item is essential on the due diligence checklist because technology is now integral to nearly every business. A flawed technical foundation can lead to operational inefficiencies, security vulnerabilities, and scalability bottlenecks, ultimately hindering growth and impacting profitability. For investors, this translates to significant financial risk.
Pros of Conducting a Technology and Operational Assessment
- Identifies Technological Competitive Advantages: Uncovers proprietary technology, innovative processes, or unique architectural designs that provide a market edge.
- Evaluates Scalability of Operations: Determines whether the company’s technology and infrastructure can handle anticipated growth without substantial reinvestment or performance degradation.
- Assesses Cybersecurity and Technical Risks: Identifies potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the company’s systems that could lead to data breaches, operational disruptions, or regulatory penalties.
- Validates Claims of Proprietary Technology: Confirms the existence and effectiveness of any claimed technological advancements.
Cons of Conducting a Technology and Operational Assessment
- Requires Specialized Technical Expertise: Effectively evaluating complex technical systems often requires hiring external experts with specific knowledge.
- Technology Landscapes Change Rapidly: Technology can become outdated quickly, making some assessments short-lived.
- Difficult to Evaluate Code or System Quality Externally: Without access to source code and internal documents, assessing the quality and maintainability of software can be challenging.
- Technical Advantages Can Be Temporary: Competitors may quickly replicate or surpass technological advancements, diminishing any initial advantage.
Real-World Examples
- Facebook/WhatsApp: Facebook’s technical due diligence of WhatsApp before acquiring it highlighted the platform’s robust and scalable architecture, a key factor in the deal.
- Microsoft/GitHub: Microsoft’s technology assessment of GitHub likely focused on the platform’s codebase, security, and community engagement, crucial aspects for its integration into Microsoft’s developer ecosystem.
- Vista Equity Partners: Vista Equity Partners, known for its technology-focused investment strategy, uses a proprietary technical assessment scorecard to evaluate potential investments. This demonstrates the importance they place on this aspect of due diligence.
Tips for Implementation
- Engage Technical Experts: Leverage external expertise to gain a deep understanding of the company’s technology.
- Review Software Development Practices: Examine the company’s development lifecycle, code repository, and documentation to assess code quality and development practices.
- Assess the Engineering Team: A strong and stable engineering team is crucial for long-term success. Consider team capabilities and turnover rate.
- Evaluate Technology Scalability: Model the impact of increased user traffic, data volume, and transaction load on the company’s systems.
- Understand Technology Dependencies: Identify reliance on third-party technologies and any associated risks.
Influences on Adoption
The importance of technical due diligence has been amplified by individuals like Marc Andreessen, whose emphasis on technology’s role in business has influenced investment strategies. Robert Smith’s technical assessment methodology at Vista Equity Partners further solidified its importance in private equity. Amazon’s focus on technical excellence has set a benchmark for operational efficiency and scalability. These influences have contributed to the widespread use of robust technical assessments in investment due diligence.
7. Customer and Sales Analysis
Customer and Sales Analysis is a crucial part of any investor’s due diligence. It provides a deep dive into the health and sustainability of a company’s revenue generation by examining its customer base, sales pipeline, customer acquisition strategy, and retention metrics. This helps investors understand not only how a company sells, but also to whom they sell, uncovering potential risks and validating growth projections. For Chief Compliance Officers, CFOs, Investor Relations Managers, and other stakeholders, this step is essential for informed investment decisions.
This analysis evaluates several key features:
- Customer concentration analysis: This identifies any over-reliance on a small number of customers, which presents a significant risk if a key account is lost.
- Sales pipeline verification: This confirms the realism of projected sales by examining the stages of deals in progress.
- Customer churn rates: These metrics measure the rate at which customers discontinue their relationship with the company, providing insight into customer satisfaction and product stickiness.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) analysis: This gauges customer loyalty and satisfaction by asking how likely they are to recommend the company.
- Sales team efficiency metrics: These evaluate the performance of the sales team in terms of conversion rates, deal size, and sales cycle length.
- Customer acquisition channels assessment: This determines the effectiveness and cost-efficiency of different marketing and sales channels.
Why This Matters
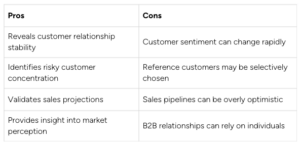
A robust customer and sales analysis reveals the stability of customer relationships, identifies potentially risky customer concentrations, validates sales projections, and provides crucial insight into market perception of the company and its products or services.
Pros and Cons of Customer and Sales Analysis
It’s important to consider both the advantages and disadvantages of this type of analysis.
Real-World Examples
- Salesforce‘s thorough customer analysis before acquiring Slack provided insights into potential integration challenges and opportunities for cross-selling.
- Bain Capital, known for its rigorous due diligence, uses structured customer interviews to assess target companies’ customer relationships and market positioning. TPG, another private equity firm, employs a similar systematic customer interview process.
Evolution and Growth in Importance
The importance of customer analysis has grown, particularly with the rise of SaaS and subscription-based businesses. Fred Reichheld’s Net Promoter Score (NPS) methodology revolutionized customer loyalty measurement. SaaS metrics pioneer David Skok’s customer analysis framework provided a structured approach to evaluating SaaS businesses. Consulting firms like Bain & Company further solidified the importance of customer due diligence with their structured approaches.
Practical Tips for Implementation
- Conduct independent customer interviews: Don’t rely solely on management-provided contacts. Seek out customers independently for unbiased perspectives.
- Analyze cohort retention data: Track retention rates for different customer segments over time to identify trends and potential churn risks.
- Review the largest customer contracts: Understand the terms and conditions of key customer agreements, including renewal clauses and pricing structures.
- Evaluate customer acquisition cost (CAC) trends: Rising CAC can indicate challenges in acquiring new customers efficiently.
- Assess sales forecast accuracy history: Compare past sales forecasts with actual results to gauge the reliability of future projections.
By thoroughly analyzing the customer and sales aspects of a potential investment, investors can gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s revenue drivers and potential vulnerabilities. This is essential for making well-informed investment decisions and mitigating risk.
8. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Evaluation
An Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) evaluation is a core element of thorough investor due diligence. It goes beyond traditional financial metrics to assess a company’s sustainability and ethical impact. For key stakeholders like Chief Compliance Officers, CFOs, and Investor Relations Managers, understanding ESG due diligence is critical for managing risk and seizing new opportunities.
This evaluation examines a company’s environmental footprint, social responsibility practices, and corporate governance structure. It looks at aspects such as:
- Environmental sustainability practices: Resource efficiency, pollution control, and efforts to mitigate climate change.
- Social impact and community relations: Labor practices, human rights policies, supply chain management, community engagement, and product safety.
- Corporate governance structure: Board composition, executive compensation, shareholder rights, transparency, and ethical business conduct.
- Diversity and inclusion policies: Representation of diverse groups, promotion of inclusive practices, and efforts to address pay gaps.
- Ethical business practices: Anti-corruption measures, fair competition, data privacy, and responsible marketing.
- ESG reporting and transparency: Disclosure of ESG performance data, adherence to reporting frameworks, and verification of information.
Why ESG Matters in Due Diligence
ESG factors can significantly affect a company’s long-term financial performance. Overlooking these factors can expose investors to reputational damage, regulatory risks, and financial losses. A strong ESG evaluation helps identify these risks and reveals a company’s values and culture.
Pros of ESG Evaluation
- Identifies Reputational and Regulatory Risks: Companies with poor ESG performance are more vulnerable to public scrutiny, consumer boycotts, and regulatory penalties.
- Aligns with Investor Focus on Sustainability: ESG investing is gaining momentum. Companies with strong ESG profiles attract responsible investors.
- Predicts Future Regulatory Compliance Issues: ESG evaluations can help anticipate emerging regulations and potential compliance challenges.
- Reveals Corporate Culture and Values: ESG performance offers insight into a company’s commitment to ethical conduct, social responsibility, and long-term value creation.
Cons of ESG Evaluation
- Varying ESG Standards: A lack of standardized metrics can make comparing and benchmarking companies difficult.
- Evolving Measurement: The field of ESG measurement is constantly developing, making consistent data difficult to obtain.
- Quantifying Financial Impact: The link between ESG and financial performance is increasingly clear, but precise measurement remains a challenge.
- Risk of “Greenwashing”: Companies may try to appear ESG-compliant without genuinely integrating sustainability into their operations.
Real-World Examples
- BlackRock: CEO Larry Fink’s annual letters highlight ESG integration in investment decisions, emphasizing sustainability for long-term value.
- TPG Rise Fund: This impact investing fund uses a rigorous social impact measurement methodology to assess the outcomes of its investments.
- KKR: KKR has developed a comprehensive ESG due diligence framework integrated into all investment decisions.
Tips for Implementation
- Use Established Frameworks: Refer to frameworks like the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) or the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) for guidance.
- Benchmark Against Peers: Compare a company’s ESG performance to its competitors to identify strengths and weaknesses.
- Verify ESG Claims: Don’t rely solely on company-reported data. Seek independent verification from third-party sources.
- Consider Future Regulatory Trends: Stay informed about emerging ESG regulations.
- Evaluate Alignment Between Values and Practices: Ensure a company’s stated ESG commitment reflects its operations and practices.
The increasing focus on ESG by prominent investors like Larry Fink and institutions like Generation Investment Management has cemented its role in finance. By incorporating a thorough ESG evaluation into your due diligence process, you gain a deeper understanding of a company’s long-term risks and opportunities, leading to informed investment decisions.
Investor Due Diligence: 8-Point Comparison
| Method | Complexity 🔄 | Resources ⚡ | Outcomes 📊 | Use Cases 💡 | Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Financial Statement Analysis | Moderate – Requires detailed financial review | High – Accounting expertise and historical data | Quantifiable insights into financial health and risk exposure | Investment evaluation in established companies | Comprehensive and data-driven valuation |
| Management Team Assessment | Moderate – Involves subjective qualitative review | Moderate – Interviews and background research | Clear picture of leadership capability and cultural fit | Evaluating startups or firms with significant leadership impact | Reveals team strengths and potential red flags |
| Market Analysis and Competitive Landscape | Moderate to High – Dependent on market data quality | High – In-depth industry research and expert insights | Strategic understanding of market potential and competitive position | Growth-oriented investments and market entry strategies | Contextualizes business scalability and competitive edge |
| Legal and Regulatory Compliance | High – Requires rigorous legal investigation | High – Legal experts and detailed document review | Identification of legal risks and confirmation of operational legitimacy | Investments in highly regulated sectors and cross-border operations | Minimizes costly legal surprises and ensures compliance |
| Business Model Validation | Moderate – Analysis of revenue models and economics | Moderate – Financial and strategic analysis inputs | Assessment of business viability, scalability, and profit potential | Early-stage ventures and emerging business models | Pinpoints hidden risks and scalability opportunities |
| Technology and Operational Assessment | High – Requires technical expertise and process review | High – Specialized technical experts and IT audits | Evaluation of operational efficiency and technology leverage | Tech-centric firms and operations requiring scalable IT infrastructure | Identifies competitive tech advantages and operational bottlenecks |
| Customer and Sales Analysis | Moderate – Based on customer data and sales metrics | Moderate – Market research and data analysis tools | Insight into revenue generation, customer retention, and market sentiment | Businesses with heavy customer reliance and dynamic sales cycles | Validates sales projections and highlights customer concentration |
| ESG Evaluation | Moderate to High – Varies with industry standards | Moderate – Sustainability reporting frameworks and data | Clarity on sustainability performance and risk of greenwashing | Companies focusing on responsible investments and sustainability goals | Aligns with modern trends and anticipates regulatory shifts |
Investing With Confidence: Your Next Steps
Thorough investor due diligence isn’t a one-off event; it’s an ongoing process. Every step, from analyzing financial statements and evaluating management teams to understanding ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) considerations and regulatory compliance, is crucial for making well-informed investment decisions. Using a comprehensive checklist that covers financial analysis, market research, legal compliance, business model validation, technology assessment, and customer analysis will provide you with the necessary insights to mitigate risk and uncover promising investment opportunities.
The investment world is constantly changing, with trends like increased regulatory scrutiny, the growth of impact investing, and the escalating importance of data security continually reshaping the due diligence landscape. Successfully adapting to these changes requires a commitment to continuous learning and the adoption of innovative tools. Staying up-to-date on best practices, emerging technologies, and regulatory changes is vital for maintaining a strong due diligence framework.
Regularly reviewing and refining your checklist, incorporating lessons learned, and seeking expert advice when needed will further strengthen your ability to navigate the complex investment market.
Key Factors for Successful Due Diligence
- Comprehensive Analysis: A thorough due diligence process should cover all aspects of the investment, from financial health to ESG factors. This comprehensive approach is essential for sound decision-making.
- Adaptability: The investment environment is dynamic. Continuous learning and adaptation to new trends and regulations are key to staying ahead.
- Technology Integration: Utilizing technology can streamline the due diligence process, improve accuracy, and reduce manual work. Tools like Blackbird can automate many aspects of due diligence.
- Collaboration: Effective communication and collaboration among stakeholders are fundamental to a successful due diligence process.
Streamlining Your Due Diligence Process
Streamlining your investor due diligence is no longer optional – it’s essential. Blackbird helps financial firms, investment funds, and regulated industries transform KYC (Know Your Customer) and investor onboarding by automating compliance workflows and significantly reducing manual effort. Features like automated document verification, AI-driven risk classification, real-time collaboration tools, and seamless integration with leading third-party screening providers enable you to accelerate due diligence, improve accuracy, and ensure compliance with evolving AML (Anti-Money Laundering) regulations – all while providing a smooth investor experience. Take control of your due diligence and invest with confidence. Visit Blackbird to learn more.