How Document Lifecycle Management (DLM) Transforms Business Efficiency and Compliance?
Published: May 29, 2025The Real-World Impact of Document Lifecycle Management
Document Lifecycle Management (DLM) is more than storage it’s a strategic approach to boost productivity, reduce costs, and ensure compliance. Learn how modern organizations leverage DLM for smarter workflows, faster retrieval, and enhanced collaboration.
Why is Document Lifecycle Management critical for modern businesses?
Effective DLM offers several key benefits:
- Improved Efficiency: Streamlined processes lead to faster retrieval times. Imagine locating the exact document you need in seconds, not hours.
- Enhanced Compliance: Detailed tracking and auditable trails ensure adherence to regulations, minimizing legal risks.
- Reduced Costs: Optimized storage and less duplication save money on physical space and digital infrastructure.
- Better Collaboration: Controlled access and version control allow for smoother teamwork, reducing errors and rework.
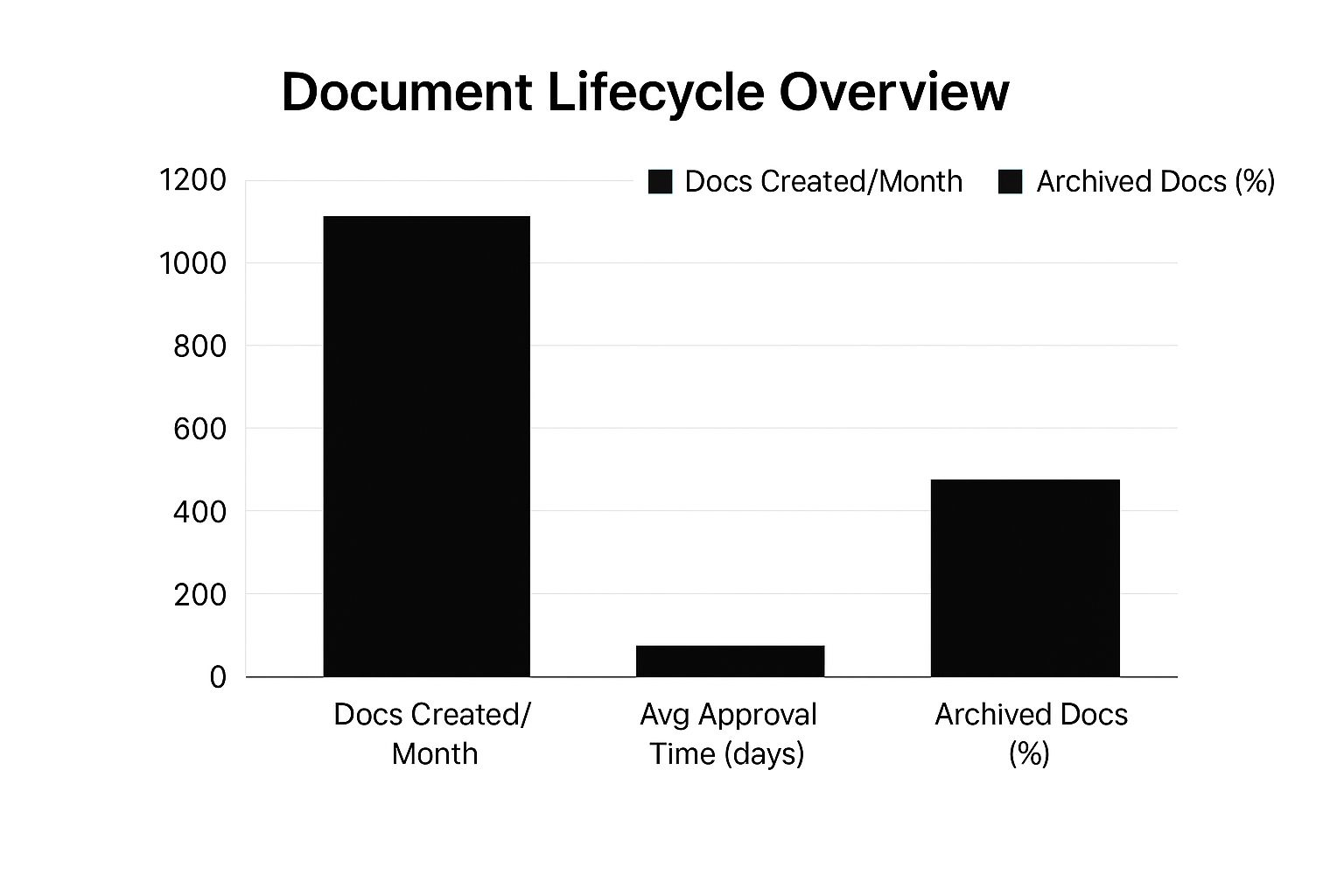
Organizations that manage their document lifecycle well consistently outperform competitors in audit readiness, information retrieval, and team collaboration. The infographic below illustrates key document metrics in a typical organization:
This data shows the volume of documents created (1200/month), the efficiency of approval workflows (3 days on average), and the effectiveness of archiving practices (75% of documents archived). These are the very metrics DLM strives to optimize. This shift to digital documentation is reflected in the broader market. The Document Management Systems (DMS) market, driven by the need for efficient digital document handling and compliance, was valued at USD 8.96 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 17.03 billion by 2029.
How is document lifecycle management different from simple document storage?
Many organizations mistake document storage for document lifecycle management. Storage is simply keeping documents; management is actively controlling them. True DLM goes beyond storage, encompassing the following:
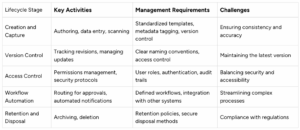
To further illustrate the stages and requirements of DLM, let’s examine the following table:
Document Lifecycle Stages and Management Requirements
This table outlines each stage of the document lifecycle and the specific management requirements for each phase.
This table outlines major activities, requirements, and challenges at each stage. By addressing these, organizations can enhance their document lifecycle management (DLM) processes.
Managing documents has clear benefits. These include lower storage costs, quicker access to information, and improved workflows. This approach views documents as valuable assets, maximizing their value and minimizing risks.
What are the tangible benefits of a strong DLM system?
A strong document lifecycle management (DLM) system goes beyond compliance. It transforms how your organization works, bringing order and improving workflows. This results in measurable gains in key performance indicators.
Streamlined Retrieval and Reduced Storage Costs
DLM speeds up document retrieval. Finding files takes seconds instead of hours. This efficiency helps employees focus on important tasks instead of wasting time searching.
DLM also cuts both physical and digital storage costs. By eliminating duplicates and using smart archiving, companies often save over 40% after adopting DLM. This frees up resources for other crucial projects, making organizations more agile.
Minimized Errors and Enhanced Collaboration
Effective version management is a key DLM feature. It significantly reduces errors and costly rework. When everyone has the latest approved document, confusion decreases. This leads to higher quality work and faster project completion.
A financial institution using DLM helps all team members get the right version of client agreements. This helps prevent legal problems. Clear version control helps collaboration. It gives everyone one source of truth and makes document sharing easier.
Strengthened Compliance and Robust Security
In today’s regulated environment, compliance is essential. DLM provides tools to meet and exceed regulatory standards. Features like permission controls, audit trails, and automated retention policies lower the risk of data breaches. They also help ensure compliance.
This proactive approach enhances security by protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. It also helps manage the document lifecycle. This protects the organization’s reputation and cuts legal risks. The Document Management Systems market is expanding, projected to reach USD 19.81 billion by 2030 with a CAGR of 13.51%. This growth highlights the increasing importance of DLM for organizations across industries. More detailed statistics can be found here.
By focusing on these advantages, organizations can unlock the full potential of document lifecycle management. DLM is about managing documents, risks, resources, and empowering teams.
What are the core components of effective DLM?
Effective document lifecycle management relies on key components that work together. These elements distinguish robust systems from basic storage solutions, giving organizations real control over their information.
Intelligent Document Capture
Manual data entry slows organizations down. Intelligent document capture automates this process. Technologies like Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and machine learning extract information from documents. This reduces manual entry and minimizes errors.
This speeds up processing and enhances accuracy. For instance, invoices can be processed automatically, pulling key data for accounting systems without human input. This dramatically cuts processing time.
Metadata Frameworks for Enhanced Searchability
Storing documents isn’t enough; they must be easy to locate. Metadata frameworks tag documents with relevant information for precise searches. This changes how employees access information.
Instead of relying on file names, metadata tags enable powerful searches across the document repository. This greatly improves retrieval efficiency.
Advanced Version Control
Collaboration suffers without proper version control. Version control tracks document changes, ensuring everyone uses the latest version. This prevents costly errors from outdated information while keeping a history for audits.
Version control simplifies collaboration, allowing multiple users to work on the same document simultaneously. This reduces the chances of conflicting changes. For optimal efficiency, consider solutions like Compresto for large file management.
Workflow Automation for Streamlined Processes
Workflow automation directs documents through the right paths. It automates approvals and removes manual handoffs. This speeds up decision-making and reduces bottlenecks.
Automated notifications keep everyone informed, ensuring timely actions and avoiding delays. For example, a contract needing multiple approvals can automatically route to each person, with reminders sent at every stage. This shortens finalization time.
Secure Archiving and Disposal
Documents shouldn’t be kept indefinitely. Secure archiving and disposal are critical. Archiving policies ensure that rarely needed documents are stored safely but remain accessible. Secure disposal methods ensure sensitive information is destroyed according to regulations. This helps lower security risks and cut storage costs.
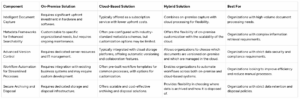
The table below shows the key differences between on-premise, cloud-based, and hybrid document management systems.
Document Management System Component Comparison
This table compares different document management system components across various deployment models, including on-premise, cloud-based, and hybrid solutions.
These core components make up effective document lifecycle management. By incorporating them, organizations significantly improve their ability to control, manage, and use the information within their documents. This leads to greater productivity, lower costs, and better compliance.
How to Build an Effective DLM Strategy
Turning theory into practice needs a solid plan. A successful document lifecycle management (DLM) strategy follows key steps. This section helps you create a practical approach.
Assessing Your Document Needs
Start by understanding your organization’s needs. A document needs assessment finds current issues and opportunities. Analyze existing processes, find bottlenecks, and discover user needs. For instance, do documents get lost or are they hard to find? Are approval processes slow? Answering these questions shapes your DLM strategy.
Establishing a Classification System
After assessing needs, create a document classification system. This system organizes documents by purpose and content. A good classification balances detail with ease of use. It should be detailed enough for accurate searching but simple enough for users to understand. Think of it like organizing a library – a good system makes finding any book easy.
Defining Retention Policies
Next, set clear retention policies. These policies dictate how long to keep documents and how to dispose of them. Retention policies must follow legal rules while avoiding unnecessary storage. This balance cuts costs and lowers the risk of data breaches. A solid DLM strategy integrates with broader software development processes. To learn more, check out the Software Development Lifecycle Phases.
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Choosing the right DLM solution is vital. Evaluate options based on your industry, company culture, and growth. Consider factors like integration with current systems, scalability, and user-friendliness. The solution should align with your long-term goals and help your organization thrive.
Implementing Change Management Strategies
Finally, establish a change management plan for a smooth transition. This includes user training, clear communication, and ongoing support. Address user resistance and encourage feedback. Successful implementation relies on user buy-in and enthusiasm for the system. Following these steps helps you create a DLM strategy that streamlines document management and ensures compliance. This organized approach builds a solid foundation for long-term success, ensuring your organization manages information well.
Proven Practices From Document Management Veterans
Skilled document management experts understand that effective processes are crucial for a successful document lifecycle management (DLM) strategy. Let’s explore some of their best practices.
Naming Conventions and Classification Schemes
Findability is crucial for effective DLM. Intuitive naming conventions and clear classification schemes help users locate documents quickly. For example, using a consistent date format (YYYYMMDD) in file names makes sorting easier.
A hierarchical classification system, like the Dewey Decimal System used in libraries, allows for detailed organization and easy retrieval. These practices turn chaotic file systems into navigable resources.
Clear and consistent naming and classification save time and reduce frustration. This structured approach is invaluable as the number of documents grows.
Metadata Tagging Strategies
Metadata tagging enhances search capabilities beyond simple file names. Assigning relevant tags unlocks powerful search options. For example, tagging contracts with client names and contract types helps users quickly find specific documents, even in large repositories.
However, too many tags can overwhelm users. Focus on the most relevant metadata to ensure efficient searching without unnecessary complexity.
Retention and Disposition Guidelines
Clear retention and disposition guidelines are essential for compliance and cost efficiency. These guidelines define how long documents are kept and how they are disposed of, following legal requirements.
Setting retention periods for each document type helps organizations save on storage costs. It also lowers the risk of keeping unnecessary data. Shredding paper documents and deleting digital files are secure ways to reduce risks. This proactive approach to information lifecycle management ensures compliance while optimizing storage.
Workflow Design Principles
Efficient workflows drive effective DLM. Automate routine tasks, like sending documents for approval. This cuts out manual handoffs and helps prevent bottlenecks.
This ensures smooth document flow, reducing delays and improving overall efficiency.
Security Protocols
Protecting sensitive information is crucial. Implement strong security protocols, including access controls, encryption, and audit trails. Access controls limit who can see or change documents. They work by user roles, so only authorized people get access.
Encryption protects data in transit and at rest. Audit trails track every document action. They create records for compliance and investigations. These measures protect sensitive information while maintaining accessibility.
A balanced approach to security safeguards information without hindering legitimate access. This robust security is essential for trust and compliance in today’s business environment.
Hidden Challenges in DLM Implementation
Even with careful planning, implementing document lifecycle management (DLM) can be tricky. This section highlights common challenges and offers practical solutions.
Tackling User Resistance
One major hurdle is user resistance. People often prefer familiar processes, even if they’re inefficient. Mandating a new system rarely excites users. Instead, focus on showing the benefits of DLM. Highlight how it simplifies daily tasks and helps them work more effectively.
Faster document retrieval can change skeptics into advocates. Meaningful engagement, not forced compliance, is key to successful DLM adoption.
Integrating With Legacy Systems
Many organizations struggle to integrate DLM with older legacy systems. Replacing these systems isn’t always feasible. Consider practical ways to integrate. You can use APIs or middleware to link the DLM system with current applications.
This phased approach helps organizations switch to DLM step by step. It avoids major changes and keeps disruptions low.
Managing Version Conflicts and Duplications
Version conflicts and duplicate documents create confusion. A strong DLM system needs features like automatic version control and duplicate detection. These features prevent users from overwriting work or creating multiple versions.
Clear naming and metadata tags reduce confusion. They make it easy to find the right version. This organized approach maintains data integrity and prevents conflicts.
Handling Growing Document Volumes
As data grows, having a scalable DLM system is essential. Cloud-based solutions often provide the best scalability, allowing storage to expand as needed.
Good archiving policies move rarely used documents to cheaper storage. This helps keep system performance high and manage costs. This proactive strategy ensures your DLM system adapts to future growth.
Balancing Security and Flexibility
Security is critical, but excessive controls can hinder productivity. The ideal DLM system balances security with operational needs. Implement role-based access controls to give users access only to necessary documents.
Use strong encryption to protect sensitive information while allowing authorized access. This lets the organization share safely with outside parties, such as investors in asset management firms. This balance is crucial in fast-paced settings, such as asset management. Clients use platforms like Blackbird. These solutions help organizations face DLM challenges. They also boost the benefits of their document management strategies.