Investor Due Diligence in 2025: 8 Key Questions Every Smart Investor Should Ask
Published: May 22, 2025Investing Smart in 2025: Mastering Due Diligence
Investor success in 2025 hinges on mastering due diligence. This checklist highlights 8 important areas. It covers financials and tech infrastructure. It helps compliance officers, CFOs, and investment pros make smarter choices.
1. Why is Financial Statement Analysis Essential?
Financial statement analysis is vital for any investor’s due diligence checklist. It includes a close look at a company’s financial statements. These are the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. This analysis provides investors with clear metrics. They can use these to evaluate a company’s financial health, profitability, and growth. It helps them understand a company’s past, present, and future.
A thorough financial statement analysis looks at three to five years of historical data.
Key features are:
-
Revenue growth trends
-
Profit margin analysis
-
Debt-to-equity ratios
-
Cash flow patterns
This helps investors find red flags. They can compare performance to industry standards and predict future outcomes. Analyzing revenue streams can reveal dependence on one client. Also, looking at debt levels can show solvency risks.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
-
Warren Buffett’s detailed analysis of Coca-Cola’s financials was key to Berkshire Hathaway’s investment. He focused on profitability, cash flow, and brand strength.
-
Venture capital firms, like Sequoia Capital, analyze startups carefully before funding rounds. This practice helps them assess young companies’ financial viability and growth potential.
Pros:
-
Provides clear metrics for evaluating performance.
-
Reveals potential financial issues.
-
Allows for industry comparisons.
-
Aids in predicting future performance.
Cons:
-
Historical data may not predict future outcomes.
-
Financials can be manipulated or presented positively.
-
Professional help may be needed for full interpretation.
-
Private companies may lack audited financial information.
Tips for Effective Financial Statement Analysis:
-
Prioritize Audited Statements: Always look for audited financial statements for better reliability.
-
Look at Trends: Check year-over-year trends, not just single numbers, to find steady patterns.
-
Benchmark Against Industry: Compare financial ratios to industry standards for context.
-
Cash is King: Pay special attention to cash flow as a reliable indicator of financial health.
-
Consistency is Key: Ensure consistent accounting methods across reporting periods for transparency.
Popularized By: Financial statement analysis matters. Benjamin Graham, author of The Intelligent Investor, and Howard Marks from Oaktree Capital highlight its importance. Credit rating agencies like Moody’s and S&P also heavily rely on this analysis.
Financial statement analysis is crucial in any investor due diligence checklist. It provides insights into a company’s financial position and potential. For Chief Compliance Officers, CFOs, and Investor Relations Managers, this analysis uncovers financial risks and opportunities, leading to better decision-making. By examining financial records closely, investors can reduce risk and find promising growth opportunities.
2. How Do You Assess a Management Team?
Another key part of the investor due diligence checklist is the Management Team Assessment. Evaluate the company’s leadership. Look at their experience, track record, integrity, and how well they execute plans. This assessment helps investors see if leaders have the skills and vision to grow and handle challenges.
A solid management team assessment has several steps:
-
Conduct background checks on key executives.
-
Review their past successes and failures.
-
Assess industry expertise.
-
Evaluate team completeness.
-
Examine succession planning.
Background checks are essential. Verify resumes and employment history using services like employment verification.
Strong leadership is key. It often makes the difference between success and failure. A strong management team can tackle challenges, use industry connections, and build trust in the company’s future.
Pros:
-
Strong leaders help the company navigate tough times and grab opportunities.
-
Industry Connections: Experienced leaders often have valuable networks.
-
Reduced Risk: Leadership integrity lowers the chance of fraud.
-
Organizational Health: Management stability often indicates a healthy organization.
Cons:
-
No Guarantees: Past success doesn’t ensure future performance.
-
Subjectivity: Evaluating leadership can be subjective.
-
Retention Risks: Key personnel may leave after an investment.
-
Succession Planning: Founder-centric companies may face succession challenges.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
-
Andreessen Horowitz: Known for supporting strong technical founders with vision.
-
BlackRock: Thoroughly evaluates management teams before significant investments.
-
Silver Lake Partners: Assessed Dell’s management deeply before their leveraged buyout.
Tips for Conducting a Management Team Assessment:
-
In-Person Meetings: Meet with key executives to evaluate their communication style.
-
Reference Checks: Check references beyond those provided for a balanced view.
-
Crisis Management: Assess how leaders handled past crises to gauge their resilience.
-
Talent Acquisition & Retention: Evaluate management’s ability to attract and keep top talent.
-
Alignment of Interests: Look for alignment between management incentives and investor interests.
Popularized By:
-
Peter Thiel (Founders Fund)
-
Reid Hoffman (LinkedIn founder and investor)
-
Bill Gurley (Benchmark Capital)
By applying these principles, investors can effectively assess management teams as part of their due diligence checklist. This thorough approach aids CFOs, Compliance Directors, and Investor Relations Managers in making informed investment decisions that can lead to higher returns.
3. Market Analysis and Competitive Landscape
A thorough market analysis and assessment of the competitive landscape is a crucial component of any robust investor due diligence checklist. This process involves deep research into the target company’s market size, growth potential, and competitive positioning. Understanding these factors allows investors to gauge the true potential of an investment, identify potential risks and opportunities, and ultimately make informed decisions. This analysis helps investors understand the company’s market opportunity, threats from competitors, and the overall industry dynamics that might affect future performance.
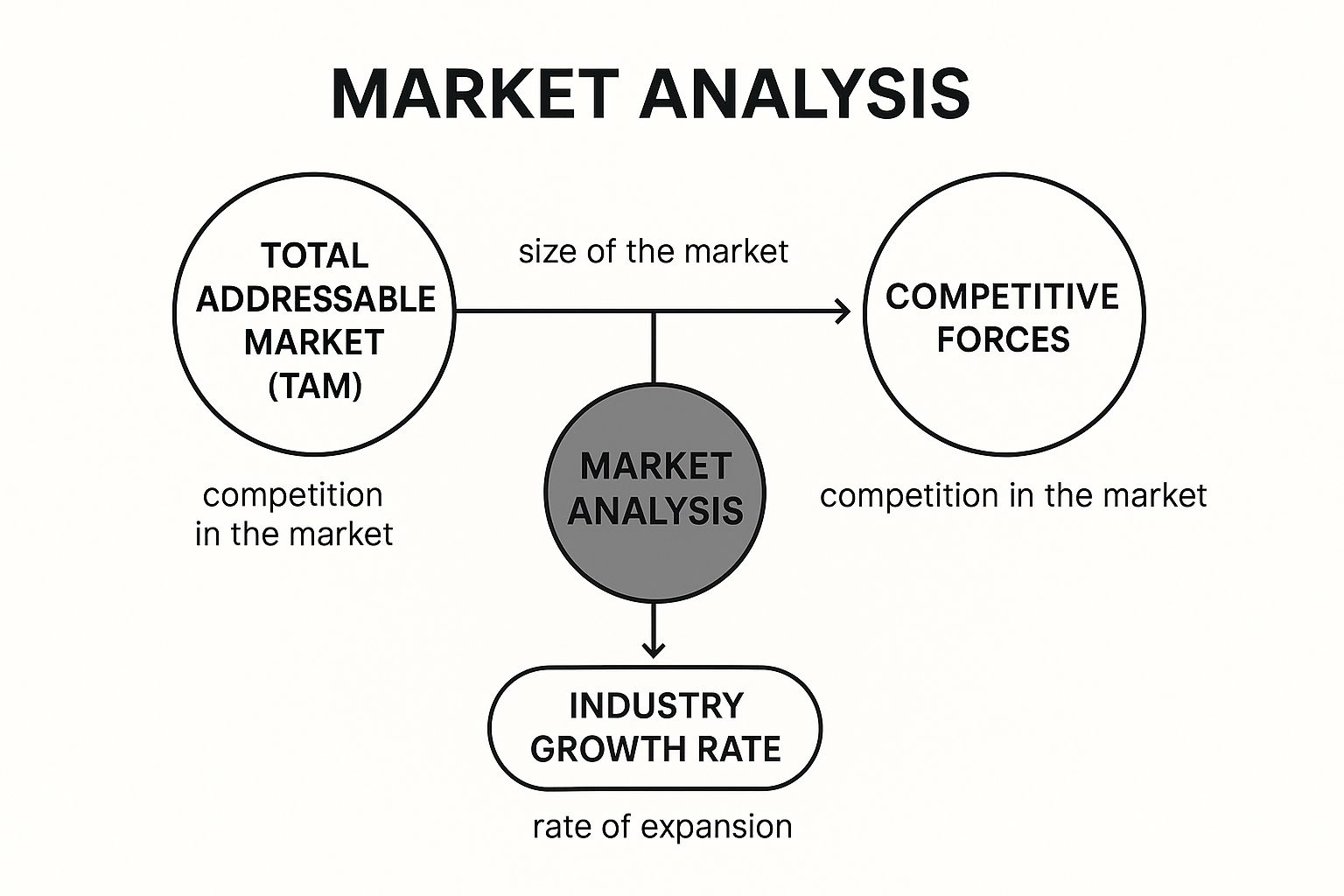
The infographic above visualizes the key concepts involved in market analysis, positioning “Market Size & Growth” as the central idea. Connected to this core concept are elements crucial for a comprehensive understanding: “Competitive Landscape,” encompassing competitor analysis and barriers to entry; “Industry Trends,” examining current and future market influences; and “Target Company,” representing its position within this dynamic ecosystem. The connections illustrate the interdependence of these factors in determining a company’s potential. For example, a large market size is less attractive if the competitive landscape is overly saturated or if disruptive trends threaten the company’s business model. The infographic emphasizes the importance of considering all these elements in conjunction for a complete market analysis.
This analysis typically involves evaluating the Total Addressable Market (TAM), analyzing market growth rates, mapping the competitive landscape, assessing barriers to entry, and analyzing industry trends to project future outlook. For instance, calculating the TAM helps determine the overall potential of the market the company operates in, while identifying key competitors and their strategies allows for a realistic assessment of the company’s market share and growth potential. Analyzing barriers to entry, such as high capital requirements or regulatory hurdles, helps understand the company’s defensibility against new entrants.
Successful examples of this approach include Softbank Vision Fund’s extensive market analysis before investing in ridesharing companies, Tiger Global’s research into e-commerce market potential in emerging economies, and Kleiner Perkins’ analysis of the cloud computing market before their early investments in the sector. These firms understood that evaluating market dynamics and competitive forces is essential for identifying promising investment opportunities and mitigating potential risks.
Pros of conducting a thorough market analysis:
- Helps determine realistic growth potential.
- Identifies potential disruption risks.
- Validates business model viability in the marketplace.
- Provides context for evaluating the company’s strategy and positioning.
Cons to consider:
- Market data may be incomplete for emerging industries.
- Disruptive innovations can rapidly change market dynamics.
- Market size estimates can be overly optimistic.
- Predicting competitive responses to the company’s strategies can be challenging.
Actionable tips for effective market analysis:
- Use multiple independent sources for market data: Triangulating information from various sources helps ensure accuracy and reduces bias.
- Speak with industry experts and potential customers: Qualitative insights from experts and potential customers can provide valuable context and validate market data.
- Analyze not just current competitors but potential future ones: Consider emerging players and disruptive technologies that could reshape the competitive landscape.
- Consider regulatory changes that might affect market dynamics: Regulatory shifts can significantly impact market size, growth, and competitive dynamics.
- Look at international markets and expansion potential: Evaluate the company’s potential to expand into new markets and the associated opportunities and challenges.
This item deserves its place in the investor due diligence checklist because it provides a foundational understanding of the market context in which the target company operates. By diligently assessing the market landscape and competitive dynamics, investors can make more informed decisions, better manage risk, and ultimately increase the likelihood of successful investments. This approach, popularized by thought leaders like Michael Porter (competitive analysis frameworks), Mary Meeker (internet trends reports), and McKinsey & Company (market sizing methodologies), remains a cornerstone of sound investment practice.
4. What’s covered in Legal & Regulatory Due Diligence?
Legal and Regulatory Due Diligence is a critical component of any robust investor due diligence checklist. It includes a detailed review of a target company’s legal documents, contracts, and intellectual property rights. It also checks compliance with regulations and any potential litigation risks. This careful process helps investors spot legal issues that could affect the company’s operations, value, and investment potential. Skipping this step can result in costly surprises after acquisition and put the entire investment at risk.
Why is Legal and Regulatory Due Diligence Essential?
This part of due diligence should be high on the checklist. It looks at the legal and regulatory situation of the target company. Finding hidden liabilities, legal disputes, or compliance issues helps investors make better decisions. This way, they can avoid major losses. A Chief Compliance Officer, Compliance Director, CFO, or Investor Relations Manager must understand legal risks. This knowledge is vital for protecting the organization’s interests.
Features of Legal and Regulatory Due Diligence:
A thorough legal and regulatory due diligence process typically includes:
-
Review of corporate formation documents: Verification of the company’s legal structure, proper incorporation, and good standing.
-
Analysis of material contracts and commitments: Examination of customer contracts, vendor agreements, leases, and other significant commitments to identify potential risks and obligations.
-
Examination of intellectual property portfolio: Confirmation of ownership, validity, and enforceability of patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets, crucial for companies relying on innovation and proprietary technology.
-
Assessment of pending or potential litigation: Evaluation of ongoing lawsuits, potential legal claims, and other disputes that could impact the company’s financial health and reputation.
-
Verification of regulatory compliance and permits: Ensuring adherence to all applicable laws, regulations, and industry-specific requirements. This is particularly important for industries with stringent regulatory oversight.
-
Review of employment agreements and labor issues: Assessment of compliance with labor laws, employment contracts, and potential labor disputes.
Pros and Cons:
Pros:
-
Identifies potential deal-breaking legal issues: Early detection of legal red flags allows investors to renegotiate terms, walk away from a deal, or implement appropriate risk mitigation strategies.
-
Helps negotiate appropriate indemnities and warranties: Provides leverage for negotiating protective clauses in the acquisition agreement to address identified legal risks.
-
Verifies ownership of key assets and IP: Confirms that the company actually owns the assets it claims, preventing future ownership disputes.
-
Prevents post-transaction legal surprises: Thorough due diligence minimizes the risk of unexpected legal issues arising after the acquisition is complete.
Cons:
-
Can be time-consuming and expensive: Requires significant effort and resources, especially for complex businesses or those operating in highly regulated industries.
-
Requires specialized legal expertise in relevant fields: Engaging specialized legal counsel is essential to navigate complex legal issues and ensure a thorough review.
-
May not uncover all potential future legal issues: Due diligence focuses on existing issues and may not predict all future legal challenges.
-
International operations add complexity to legal review: Dealing with different legal systems and regulations adds another layer of complexity to the process.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
-
Facebook’s legal due diligence of WhatsApp before its $19 billion acquisition ensured a smooth transaction and addressed potential data privacy concerns.
-
Microsoft’s extensive IP review before acquiring GitHub was crucial given the platform’s vast repository of open-source code.
-
Private equity firm KKR’s regulatory compliance examination of portfolio companies is a standard practice to mitigate regulatory risks and ensure compliance.
Actionable Tips for Conducting Legal and Regulatory Due Diligence:
-
Engage specialized legal counsel: Seek expert advice in relevant areas such as intellectual property, antitrust, and regulatory compliance.
-
Create a comprehensive legal due diligence checklist: Develop a detailed checklist to ensure all critical areas are covered.
-
Pay special attention to change-of-control provisions in contracts: Identify potential issues arising from the change in ownership.
-
Verify ownership chains for key intellectual property: Thoroughly document the ownership history of crucial IP assets.
-
Review litigation history for patterns of business conduct: Identify potential recurring legal issues and assess their impact on the business.
Popularized By:
Top law firms such as Skadden Arps, Latham & Watkins, and Wilson Sonsini Goodrich & Rosati play a vital role in shaping best practices for legal due diligence, especially in Silicon Valley. The American Bar Association’s M&A guidelines also provide valuable guidance on the process. By adhering to the principles of thorough legal and regulatory due diligence, investors can significantly mitigate risk and make more informed investment decisions.
5. Business Model Validation
Business model validation is a critical component of any investor due diligence checklist. It includes a careful look at how a company makes money, stays profitable, and builds lasting competitive edges. This evaluation shows investors if the business model works well. It checks if it can grow and if the unit economics are strong enough for long-term success. Essentially, it answers the fundamental question: Can this business make money, and can it continue to do so in the long run?
This step should be a key item on the investor due diligence checklist. It goes beyond just looking at past financials. It looks at how the business works. This gives clues about its chances for success in the future. Key features of this analysis include dissecting revenue streams and their diversification, assessing unit economics (Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Lifetime Value (LTV), and margins), evaluating the pricing strategy, determining scalability potential, analyzing the sales cycle and customer acquisition process, and scrutinizing recurring revenue models.
Chief Compliance Officers, CFOs, Investor Relations Managers, and other stakeholders must grasp the business model’s strength. This understanding is key for managing risks and meeting regulations. A validated business model provides greater confidence in the investment’s long-term prospects.
Benefits of Business Model Validation:
-
Validates assumptions underlying financial projections: It ensures that the financial forecasts are grounded in realistic assumptions about the business’s operations.
-
Identifies key drivers of profitability: Pinpoints the factors that contribute most significantly to the company’s bottom line.
-
Assesses sustainability of the business beyond initial growth: Determines whether the business can maintain its growth trajectory over the long term.
-
Helps understand capital efficiency: Evaluates how effectively the company utilizes its capital to generate revenue and profits.
Pros and Cons of Business Model Validation:
Pros:
-
Offers a comprehensive understanding of the business’s revenue generation mechanics.
-
Helps identify potential risks and vulnerabilities in the business model.
-
Provides insights into the company’s competitive advantages.
-
Supports informed investment decisions based on sound data and analysis.
Cons:
-
Early-stage companies often lack a long operating history. This makes it tough to validate models. So, they must focus more on market research and analyzing competitors.
-
Business models can change quickly in active markets. So, they need regular monitoring and adjustments to the validation process.
-
Difficult to predict customer behavior and adoption: Market research and testing are essential to mitigate this challenge.
-
Competitors may force model adjustments: Staying agile and responsive to competitive pressures is key.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
-
Sequoia Capital’s in-depth analysis of subscription economics played a crucial role in their successful investment in Zoom.
-
Benchmark’s evaluation of Uber’s marketplace model was cited as a contributing factor in their early investment decision
-
Accel Partners’ evaluation of Slack’s freemium conversion metrics helped them recognize the platform’s potential for rapid growth.
Actionable Tips for Conducting Business Model Validation:
-
Focus on cohort analysis: Understand customer behavior and retention over time by analyzing specific groups of customers acquired during the same period.
-
Analyze gross margins and contribution margins separately: This provides a clearer picture of profitability at different levels.
-
Test the sensitivity of the model to different market conditions: Assess the impact of potential changes in the market on the business’s performance.
-
Evaluate whether growth requires proportional cost increases: Determine the scalability of the business model.
-
Compare unit economics to industry benchmarks: Gain insights into the company’s performance relative to its competitors.
Popularized By: The concepts and frameworks related to business model validation have been significantly influenced by thought leaders like Bill Gurley (unit economics essays), Alex Osterwalder (Business Model Canvas), Eric Ries (Lean Startup methodology), and David Skok (SaaS metrics frameworks).
By incorporating business model validation into your investor due diligence checklist, you can make more informed investment decisions based on a thorough understanding of the company’s potential for sustainable growth and profitability. This rigorous approach is essential for mitigating risk and maximizing the potential for successful investments.
6. Technology and Operational Assessment
This crucial step in the investor due diligence checklist, the Technology and Operational Assessment, delves into the very engine room of a company: its technology infrastructure, product development capabilities, operational processes, and scalability. For investors, understanding these core components is essential for gauging the long-term viability and potential for growth. This assessment provides insights into the technical foundation of the business and its ability to execute efficiently, especially during periods of rapid expansion. It’s a critical element of any robust investor due diligence checklist, particularly in today’s digitally driven world.
How it Works:
A Technology and Operational Assessment typically involves a multi-faceted approach, encompassing several key areas:
-
Technology Stack Review: Analyzing the chosen technologies, programming languages, frameworks, and databases used by the company to build and maintain its products and services. This reveals the modernity, maintainability, and scalability of the tech stack.
-
Code Quality and Architecture Assessment: Evaluating the quality, structure, and organization of the codebase. This helps identify potential technical debt, security vulnerabilities, and maintainability issues.
-
Security and Data Privacy Evaluation: Examining the company’s security protocols, data protection measures, and compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA). This is paramount in today’s environment of increasing cyber threats and data breaches.
-
Technical Debt Analysis: Quantifying the implied cost of rework caused by choosing an easy (limited) solution now instead of using a better approach that would take longer. High technical debt can hinder future development and innovation.
-
Supply Chain and Operational Efficiency Review: Analyzing the company’s supply chain, procurement processes, and operational workflows to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and potential areas for improvement.
-
Product Development Processes and Roadmap: Understanding the company’s approach to product development, including its roadmap, release cycle, and ability to innovate and adapt to market changes.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
-
Google Ventures, known for its rigorous due diligence process, frequently employs deep technical assessments before investing in startups, examining the scalability and security of their technology.
-
Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foods involved an extensive operational assessment to understand the grocery chain’s logistics, supply chain, and inventory management systems.
-
Microsoft’s acquisition of GitHub included a thorough evaluation of GitHub’s infrastructure to ensure its ability to support a growing user base and integrate with Microsoft’s existing services.
Pros:
-
Identifies potential technical limitations to scaling: Uncovers bottlenecks before they impede growth.
-
Assesses competitive technical advantages: Highlights any technological edge the company possesses.
-
Evaluates innovation capabilities: Determines the company’s ability to adapt and evolve its technology.
-
Helps identify potential integration challenges: Especially important for mergers and acquisitions.
Cons:
-
Requires specialized technical expertise: Investors may need to engage external consultants.
-
Technology evolves rapidly, making assessments quickly outdated: Continuous monitoring is essential.
-
Difficult to evaluate proprietary technologies: Limited access can hinder a thorough assessment.
-
Internal systems may appear more robust than they are: On-site testing and validation are crucial.
Tips for Investors:
-
Involve technical experts in the due diligence process: Engage experienced software engineers and security professionals.
-
Request architecture diagrams and system documentation: Gain a clear understanding of the technical landscape.
-
Assess the quality and retention of the engineering team: Evaluate the team’s skills, experience, and stability.
-
Test scalability under various growth scenarios: Simulate increased user traffic and data volume.
-
Evaluate security practices and previous incidents: Understand the company’s vulnerability to cyber threats.
Why this Item Deserves its Place in the List:
In the modern business landscape, technology is often the backbone of a company’s operations and competitive advantage. A thorough Technology and Operational Assessment provides investors with the critical information needed to assess the true value and potential risks of an investment. It ensures a deeper understanding of a company’s ability to execute, scale, and innovate—essential factors for long-term success. This is particularly crucial for CFOs, Investors Relations Managers, Heads of Compliance, Compliance Directors, and Chief Compliance Officers who need to understand the inherent risks and opportunities associated with a company’s technical infrastructure. Failing to conduct a thorough technical and operational assessment can expose investors to unforeseen technical risks and hinder their ability to make informed investment decisions. This item’s placement in the investor due diligence checklist underscores its critical importance in today’s market.
7. Why is Customer Analysis a must?
Customer analysis is a crucial component of any robust investor due diligence checklist. This process involves a thorough examination of a company’s customer base to understand the quality, sustainability, and potential future of its revenue streams. It helps investors gauge the true market traction of the company and validate product-market fit, ultimately informing investment decisions. This step deserves a prominent place on the checklist because it offers a direct view into the health of the business beyond the financials, providing a qualitative assessment of its long-term viability.
How it Works:
Customer analysis delves into various aspects of the customer lifecycle, including:
-
Customer Concentration Analysis: Identifying key customers and assessing the risk associated with over-reliance on a small number of accounts. High customer concentration can signify revenue vulnerability if a key account is lost.
-
Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Satisfaction Metrics: Gauging customer satisfaction and loyalty using metrics like NPS provides insights into the overall customer experience and potential for future growth through referrals and repeat business.
-
Churn Analysis and Retention Strategies: Understanding customer churn rates and the effectiveness of retention strategies reveals the stability of the customer base. Low churn rates and proactive retention efforts indicate a healthy and sustainable business model.
-
Customer Acquisition Channels and Effectiveness: Evaluating the cost and efficiency of customer acquisition channels reveals the scalability of the business and the potential for future growth.
-
Contract Terms and Renewal Patterns: Analyzing contract terms and renewal rates helps project future revenue and assess the predictability of the business.
-
Customer Interviews and References: Directly interacting with customers provides invaluable qualitative insights into their needs, preferences, and overall satisfaction with the company’s products or services.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Private equity firms, such as Thoma Bravo, NEA, and Vista Equity Partners, regularly conduct thorough customer analysis during their due diligence. Thoma Bravo, for example, talks to customers and reviews contract data before investing in software companies. NEA frequently uses customer interviews for late-stage SaaS investments, and Vista Equity Partners has developed a proprietary customer retention analysis methodology.
Actionable Tips for Investors:
-
Request blind customer satisfaction surveys: This helps ensure unbiased feedback and provides a more accurate picture of customer sentiment.
-
Analyze cohort retention rates over multiple years: Tracking retention rates over time provides a deeper understanding of customer loyalty and the long-term viability of the business.
-
Speak directly with customers, not just those suggested by the company: This allows for a more objective assessment of customer satisfaction and helps uncover potential issues that the company might not readily disclose.
-
Look for evidence of expanding customer relationships over time: Growth within existing accounts (e.g., upselling, cross-selling) indicates strong customer satisfaction and potential for future revenue growth.
-
Assess sensitivity to price changes: Understanding how customers react to price increases provides insights into the value proposition and pricing power of the company.
Pros:
-
Reveals dependence on key customers
-
Provides insights into real market traction
-
Helps validate product-market fit
-
Identifies potential revenue vulnerabilities
Cons:
-
Selected customer references may be biased
-
Historical retention may not predict future loyalty
-
Limited data available for early-stage companies
-
Customer needs and preferences evolve
Popularized By:
Fred Reichheld created the NPS. HubSpot focuses on customer investment. Gainsight has customer success methods. Together, they boost the importance of customer analysis in investing.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
Customer analysis should be an integral part of the due diligence process for any investment, regardless of the stage or industry. Customer retention is crucial for businesses with recurring revenue models, like SaaS companies. This is key for long-term success. This approach lets investors look past financial statements. They can better understand what really drives the business. This knowledge leads to smarter investment choices.
8. ESG and Risk Assessment
ESG and Risk Assessment is a crucial component of any robust investor due diligence checklist. It looks at more than just financial numbers. It evaluates a company’s Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance. It also looks at other risks that could impact long-term sustainability, operational strength, and overall value. This approach recognizes that a company’s financial success connects to its responsible actions. It also depends on how well it handles various environmental, social, and governance challenges. Adding ESG analysis to your investor due diligence checklist is key. It helps you grasp potential investment risks and opportunities better.
How it Works:
ESG and risk assessment involves evaluating a company’s performance and exposure across a range of non-financial factors. This includes analyzing its:
-
Environmental impact and sustainability practices: This covers areas such as resource efficiency, pollution control, greenhouse gas emissions, and climate change adaptation strategies.
-
Social responsibility and labor practices: Key considerations include employee relations, human rights, supply chain management, community engagement, and product safety.
-
Corporate governance structure and policies: This encompasses board composition, executive compensation, shareholder rights, ethical conduct, and transparency.
-
Cybersecurity and data protection measures: Assessing a company’s vulnerability to cyberattacks and its data privacy practices is critical in today’s digital landscape.
-
Regulatory compliance and potential changes: Understanding existing and forthcoming regulations relevant to the company’s industry and operations is vital.
-
Reputational risk assessment: Analyzing how a company manages its reputation and its exposure to potential controversies.
Successful Implementation Examples:
-
BlackRock: The world’s largest asset manager has fully integrated ESG considerations into its investment process, advocating for sustainable practices and engaging with portfolio companies on ESG issues.
-
KKR: The global investment firm conducts rigorous environmental impact assessments before making infrastructure investments, recognizing the crucial role of environmental sustainability in long-term value creation.
-
TPG Rise Fund: This impact investing platform has developed a sophisticated social impact measurement methodology to quantify the positive social and environmental outcomes of its investments.
Actionable Tips for Investors:
-
Utilize established ESG frameworks: Frameworks like the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) and the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) provide standardized metrics and reporting guidelines.
-
Look beyond formal policies: Investigate actual practices and verify the implementation of stated ESG commitments.
-
Consider industry-specific ESG factors and benchmarks: Different industries face unique ESG challenges and opportunities. Tailor your assessment accordingly.
-
Evaluate the company’s approach to emerging risks: Consider factors like climate change, resource scarcity, and evolving social expectations.
-
Assess board diversity and independence: A diverse and independent board can enhance oversight and strategic decision-making regarding ESG issues.
Pros of ESG Integration:
-
Identifies non-financial risks that could impact valuation: ESG factors can significantly influence a company’s long-term financial performance.
-
Aligns investments with ethical and sustainability goals: Investors can integrate their values into their investment decisions.
-
Helps predict potential regulatory challenges: Proactive ESG assessment can anticipate future regulatory changes and mitigate potential compliance risks.
-
Can improve long-term investment performance: Studies suggest a positive correlation between strong ESG performance and financial returns.
Cons of ESG Integration:
-
ESG metrics can be difficult to quantify: Standardization is still evolving, making comparisons across companies challenging.
-
Standards vary across industries and regions: A consistent global framework for ESG reporting is yet to be fully realized.
-
May create tension with short-term profit maximization: Some ESG initiatives may require upfront investments that could impact short-term profitability.
-
Disclosure quality varies widely among companies: Transparency and data availability remain a challenge in ESG reporting.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
ESG and risk assessment must be key parts of every investment due diligence. This is true for all asset classes and investment strategies. It is particularly relevant for long-term investors focused on sustainable value creation. Chief Compliance Officers, Heads of Compliance, Compliance Directors, CFOs, and Investor Relations Managers must understand and use ESG factors. It’s crucial now. It’s not just good practice; it’s a regulatory requirement and what stakeholders expect. Investors can better decide by evaluating a company’s ESG performance. This helps them reduce risks and spot opportunities for long-term growth and impact. Investors risk financial and reputational damage if they ignore ESG factors today.
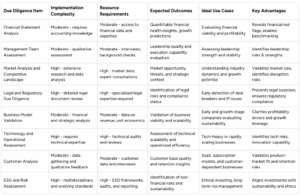
Investor Due Diligence Checklist Comparison
Streamlining Due Diligence with Blackbird
Conducting a thorough investor due diligence checklist, encompassing everything from financial statement analysis and management team assessments to market analysis and legal reviews, is essential for supporting risk-aware investment decisions and aiming for more informed outcomes. This checklist, covering key areas like business model validation, technology assessment, customer analysis, and ESG considerations, provides a robust framework for informed investment decisions. Mastering these elements allows you to confidently navigate the complexities of the investment landscape, identifying potential red flags and uncovering hidden opportunities.
The key takeaway here is that comprehensive due diligence is not just a box-checking exercise; it’s a strategic imperative. By diligently examining each item on your investor due diligence checklist – from financial health to operational efficiency and regulatory compliance – you’re building a foundation for sustainable investment success. This proactive approach helps reduce potential risks, improve transparency, and support sound portfolio oversight.
For Chief Compliance Officers, Heads of Compliance, Compliance Directors, CFOs, and Investor Relations Managers, the benefits are clear: improved regulatory compliance, more efficient workflows, and more informed investment decisions. Moving forward, prioritize implementing the insights from this checklist. Start by evaluating your current due diligence process and identifying areas for improvement.
Navigating the complexities of investor due diligence can be challenging. Blackbird, a KYC platform designed for asset management firms, simplifies this process by streamlining document collection, automating workflows, and enhancing security. From managing complex, high-touch use cases to ensuring regulatory compliance, Blackbird empowers investors with efficiency and control, allowing them to focus on what matters most—making informed investment decisions.
By embracing a robust investor due diligence checklist and leveraging innovative solutions like Blackbird, you’re not just protecting your investments—you’re building a future of informed, strategic, and sustainable growth.