Why RegTech Is the New Competitive Edge for Private Market Firms
Last Revised: September 29, 2025At a Glance
Compliance in private markets is shifting from a burden to a strategic advantage. With investors across multiple jurisdictions and rising regulatory demands, RegTech offers firms a faster, more efficient way to stay compliant and investor-ready.
What is Financial Compliance and Why Is It Strategic Now?
For private market asset managers, compliance now extends across multiple jurisdictions, investor types, and fund structures — shaped by KYC, AML, and cross-border due diligence requirements. Failures in this environment can delay fundraising, increase costs, or undermine trust with limited partners (LPs).

RegTech offers firms a faster, more efficient way to stay compliant and investor-ready.
What Are the Real Costs of Non-Compliance in the Private Market?
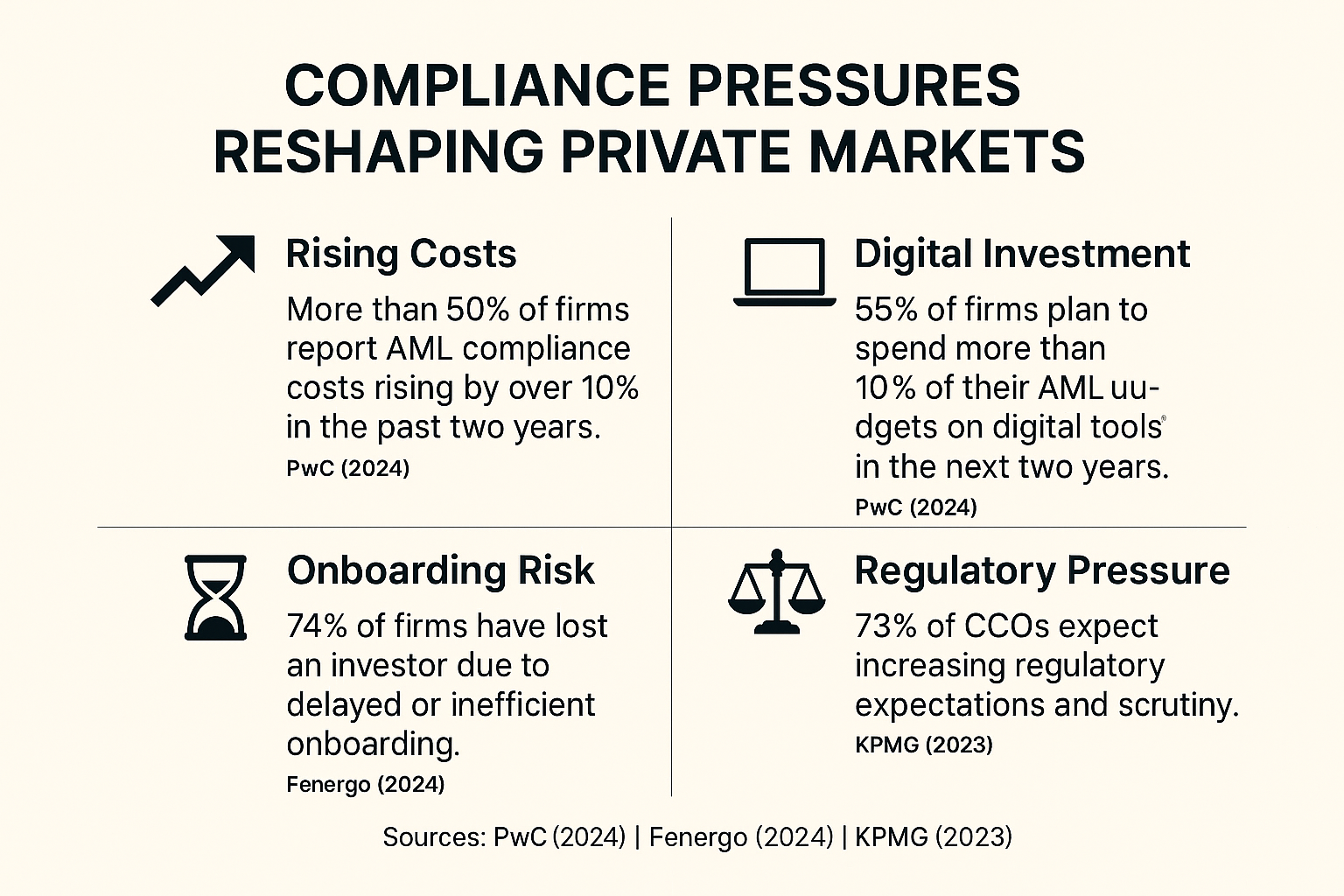
Compliance costs are on the rise: according to PwC’s 2024 EMEA AML Survey, more than half of firms reported AML compliance costs increasing by over 10% in the last two years. But non-compliance in the private market carries significant risks that go beyond fines. For fund managers and administrators, the consequences can directly impact investor relationships and fundraising success:
- Reputational Damage: LPs and placement agents may lose confidence if compliance issues surface, making future fundraising more difficult.
- Missed Commitments: Lengthy or inconsistent onboarding processes can lead investors to delay or withdraw commitments. These risks are not hypothetical: Fenergo’s 2024 report says that 74% of firms have lost investors due to delayed or inefficient onboarding.
- Operational Disruptions: Remediation efforts, investor re-papering, or audit findings can divert resources and slow deal execution.
- Regulatory Penalties: Breaches of KYC/AML, FATCA/CRS, or SEC/AIFMD requirements can result in fines and increased scrutiny from regulators.
Efficient, well-documented compliance processes reduce these risks and safeguard both the firm’s reputation and its ability to raise capital.
The Shift Towards Proactive Compliance
Compliance in the private market is moving from a reactive function, focused only on avoiding penalties, to a proactive discipline that directly shapes fundraising success.
Fund managers today must anticipate evolving regulatory requirements across multiple jurisdictions, with pressure only set to increase: KPMG’s “Anticipating More Scrutiny” report shows that 73% of Chief Compliance Officers expect heightened regulatory expectations in the upcoming future.This includes heightened SEC scrutiny in the U.S., AIFMD and ESG reporting in the EU, and AML obligations in fund domiciles such as Cayman, Luxembourg, and Ireland. At the same time, global initiatives like FATF, FATCA, and CRS demand consistent, auditable investor due diligence.
A proactive approach gives firms more than just risk protection. It reduces fundraising friction by streamlining investor onboarding, ensures smoother audits, and enhances LP trust. Technology and automation play a critical role here — replacing manual document chasing with centralized workflows that flag risks early and keep investor files always audit-ready.
How Can Firms Turn Compliance Into a Competitive Advantage?
In the private market, compliance is often viewed as a cost of doing business — but the most successful firms are using it to gain an edge. A streamlined compliance process signals professionalism to LPs, accelerates onboarding, and reduces the risk of last-minute issues during fundraising.
For fund administrators, technology-driven compliance can also improve service quality and scale — handling complex multi-entity structures, cross-border tax forms, and AML reviews without adding headcount. This creates a better investor experience and strengthens relationships.
When compliance is integrated into core workflows, rather than treated as a box-ticking exercise, it becomes a differentiator in winning and retaining institutional capital.
Compliance Pressures Are Reshaping the Private Market
The Rise of RegTech
Regulatory Technology (RegTech) is reshaping how private market firms approach compliance. Instead of fragmented workflows spread across spreadsheets, investor portals, and email trails, RegTech consolidates compliance into a single platform — reducing duplication and manual breaks in process.
This shift is also reflected in industry spending: PwC’s EMEA AML survey found that 55% of firms plan to allocate more than 10% of their AML budgets to digital tools over the next two years — signaling that technology-driven compliance is no longer optional.
AI-driven solutions can:
- Accelerate investor onboarding by automating KYC/AML checks and tax form validation.
- Reduce errors and manual effort by centralizing document management across multiple funds and jurisdictions.
- Enhance transparency with centralized records and automated reporting.
- Flag risks early through continuous monitoring, rather than relying on periodic manual reviews.
For the private market, where investors are often spread across multiple geographies and structures, RegTech provides a scalable way to meet regulatory requirements without adding compliance headcount.
What Are the Top RegTech Applications in the Private Market?
RegTech solutions are delivering tangible impact in areas that matter most to private market firms:
- KYC and AML Automation: Streamlines investor identification, sanctions checks, and document validation — reducing exceptions, manual escalation, and onboarding delays.
- Regulatory Reporting: Streamlines recurring filings such as Annex IV (AIFMD), Form ADV/PF (SEC), FATCA, and CRS, reducing the risk of missed deadlines and manual errors.
- Operational Risk Monitoring: Provides real-time visibility into compliance tasks, from pending investor approvals to incomplete document sets — ensuring issues are flagged before they become audit findings.
- Audit-Ready Recordkeeping: Centralizes compliance evidence and creates an accessible audit trail, making regulatory inspections and LP due diligence reviews far more efficient.
By focusing on these areas, RegTech enables private market firms to scale compliance processes without scaling their teams.

RegTech enables private market firms to scale compliance processes without scaling their teams.
Implementing RegTech: What Are the Challenges and Considerations?
While RegTech offers clear benefits, private market firms must navigate a few practical challenges when adopting new technology:
- Cost Trade-offs: Implementing technology requires upfront investment, but for most firms the real alternative is hiring more compliance staff. Scalable automation often proves more cost-effective over time.
- Integration with Existing Workflows: Fund managers and administrators already rely on CRMs, investor portals, and data rooms. New compliance platforms must integrate seamlessly to avoid duplicating work or fragmenting investor information.
- Specialized Talent: Compliance professionals with both regulatory knowledge and comfort with new platforms are in short supply. Firms that invest in training or choose intuitive tools will adapt more smoothly.
The good news: with the right approach, these challenges are manageable. Platforms like Blackbird automate KYC, AML, and due diligence in one place — helping firms reduce manual work, improve audit readiness, and scale without adding headcount.
The Bottom Line
For fund managers and administrators, proactive compliance is now a competitive differentiator. By embracing RegTech, firms can reduce operational drag, protect against regulatory risk, and deliver a smoother investor experience. The shift is clear: technology is no longer optional — it’s the key to scaling compliance in private markets efficiently and credibly.
Why Blackbird?
Blackbird delivers an AI-first RegTech solution built specifically for private market firms. By unifying KYC, AML, and Due Diligence in one seamless platform, we help fund managers and administrators streamline investor onboarding, stay audit-ready, and scale compliance without adding headcount.
Want to see it in action? Book a demo with our team.
For more insights (and the occasional KYC meme), follow us on LinkedIn.
About the Author
Linoy Doron is a Content Strategist at Blackbird, where she translates complex fintech and compliance topics into clear, actionable insights. With a strong background in technology, SaaS, and UX, she crafts narratives that connect product value to the real needs of asset managers in the private market.